A revolution in how robots see the world.
Lightweight, low power and easy‑to‑use depth cameras that give robots the ability to navigate landscapes, avoid obstacles and recognize objects, people and more.
The world of computer vision in robotics comes into focus.
When robots can see, measure, analyze, and respond to their environment, a whole new world of possibilities opens up. To bring these possibilities to life, the robotics industry is increasingly adopting computer vision technology which allows robots to sense depth, navigate landscapes, and recognize objects, people, and scenes. In the last several years alone, the demand for computer vision technology that is reliable and performs across a variety of conditions has grown rapidly.
Depth driven robotics.
All kinds of robots use Intel RealSense depth cameras. Here are some of the main categories where you can find robots using depth.
Wide variety of use cases.
The high-resolution imaging and depth sensing technology of the Intel RealSense cameras allow them to deliver a full range of computer vision capabilities specifically targeted for robotics developers. For high precision middle range applications, choose the D415. For close range applications select the D405. If your application is fast‑moving or outdoors, select either the D435, D435i or D435f, and for longer range applications, the D455 is perfect.
Collision Avoidance
Collision avoidance
High frame rate and depth accuracy provides the data needed, when it’s needed, to avoid obstructions. The computer vision solution of choice for robot cleaners and other automated industrial use cases that require collision avoidance. Pick and place robots are able to extract objects from bins without the object hitting the sides of the bin. Automated inventory robots navigate store aisles and avoid running into aisles, carts, or customers.
Object Detection
Object Detection
Distinguishes foreground objects from background and provides the ability to measure and understand shapes. Factory robots use high resolution imagery to distinguish between a variety of objects. Pick and place robots distinguish between a variety of objects in a bin and adjust picking pressures based on the object’s identity. Greeting robots in the retail space use object detection capability to identify and track objects and interact with consumers.
Volumetric Measurement
Volumetric Measurement
Measures objects in all three dimensions simultaneously and accurately with low measurement error. Factory robots use volumetric data to improve efficiency in packaging, placement, and storage applications. Robots in shipping facilities can determine the volume of boxes and of empty storage slots and manage inventory more efficiently. Retail robots measure empty shelf space for inventory restocking.
SLAM Tracking
SLAM Tracking
Low latency, low power, high quality localization and mapping allows robots to quickly calibrate location. Industrial delivery robots use tracking capability for path planning that enables them to move more efficiently through space. Warehouse delivery robots navigate delivery routes and keep track of their location. Inventory robots utilize mapping technology to navigate store aisles and keep track of their location.
Customer Stories

Automated warehouse order fulfillment
RightPick2 robots use Intel RealSense cameras, to quickly identify items to be able to automatically handle them at high speeds with high reliability.

Robotic DevKits
UP Bridge the Gap Partners with Intel to Introduce Game Changing Robotic Development Kits

Industry-changing mobile delivery solutions
TUG Robots use Intel® RealSense™ technology to help guide autonomous delivery robots in the manufacturing, healthcare, and hospitality industries.

The new generation of in-store retail robotics
Simbe's autonomous inventory robot Tally captures inventory and e-commerce grade insights to allow retailers to optimize their in-store operations.
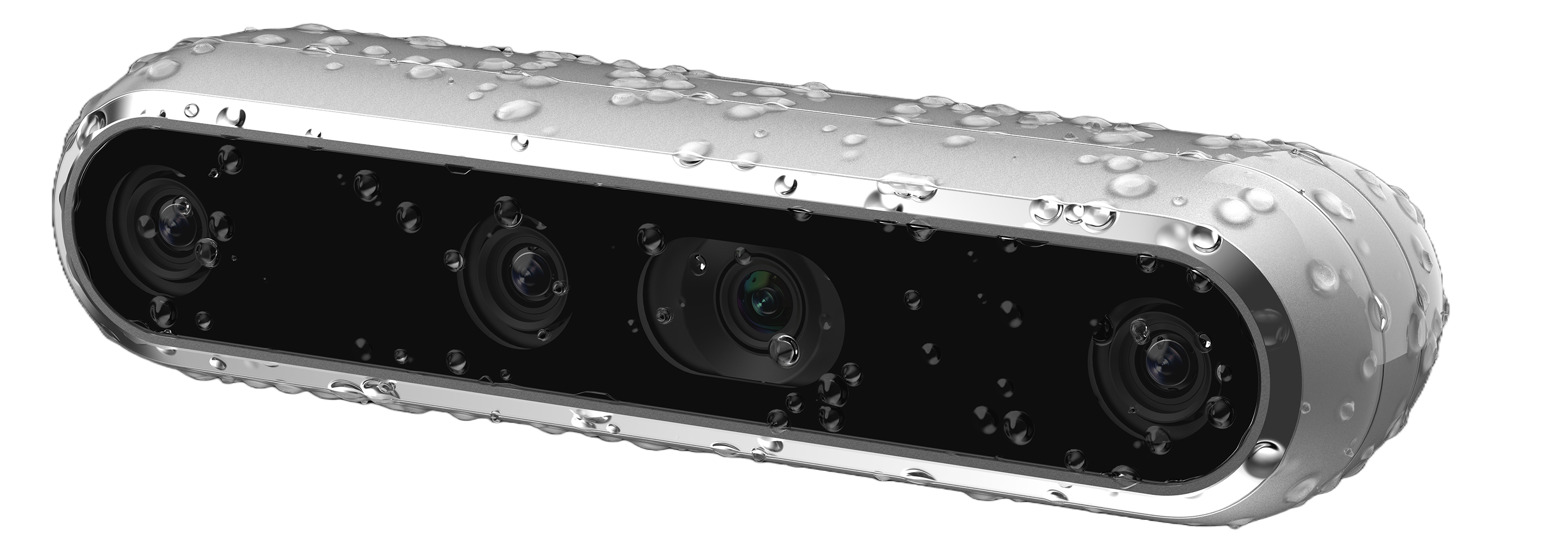
A Robust Lineup.
The Intel RealSense family of cameras is the broadest product line of computer vision cameras on the market, with a range of indoor and outdoor options that meet all the needs of today’s robotics engineers.








Developers
Start developing with Intel RealSense SDK 2.0.
Our open‑source SDK 2.0 offers a variety of wrappers supporting popular programming languages and platforms.